
Chemical Process
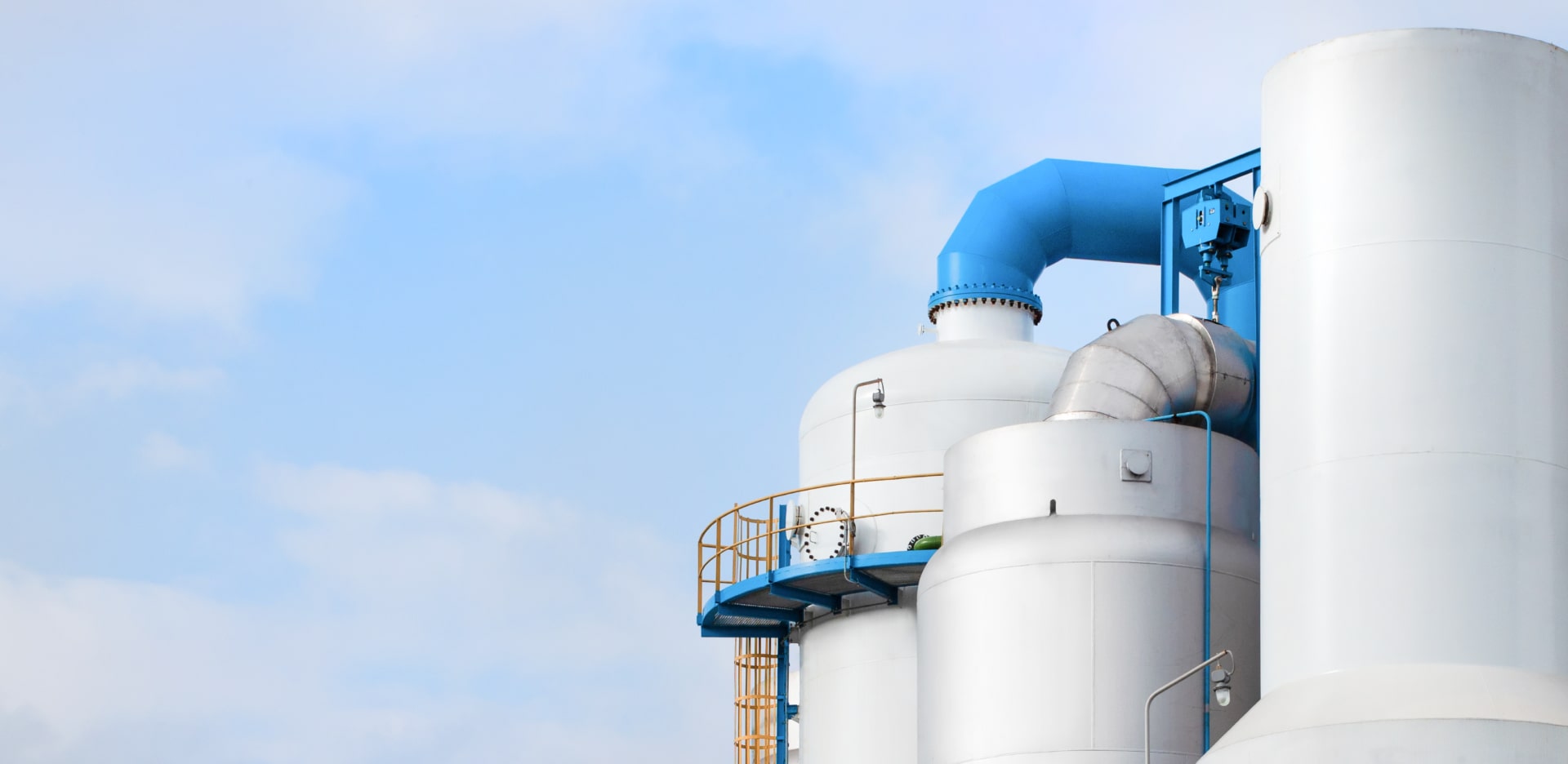
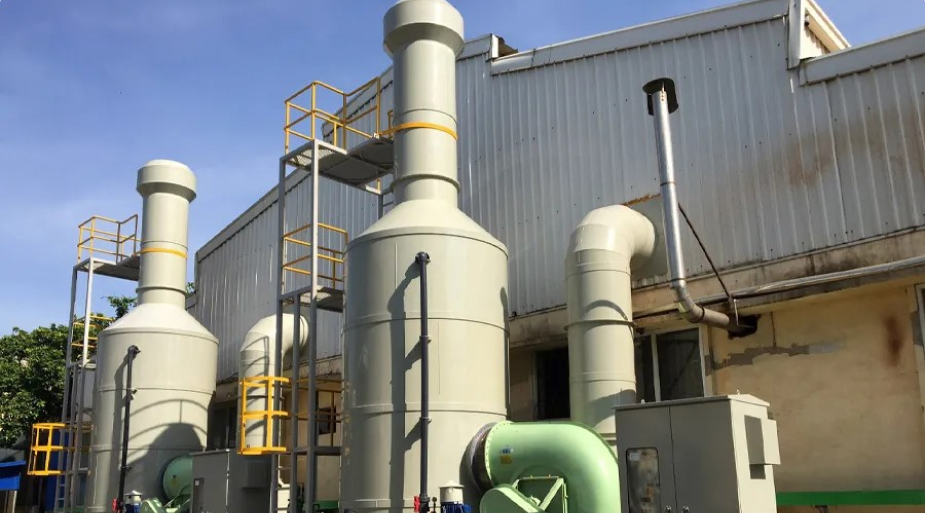
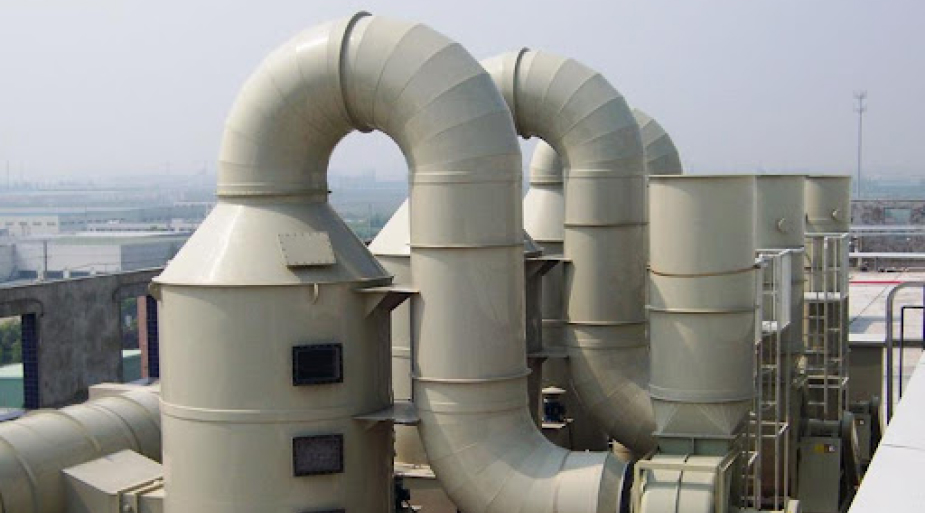
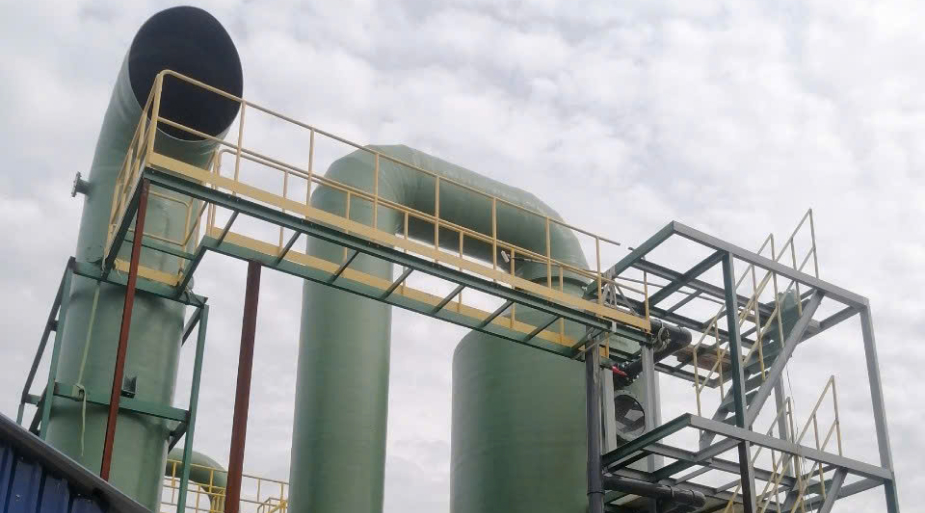
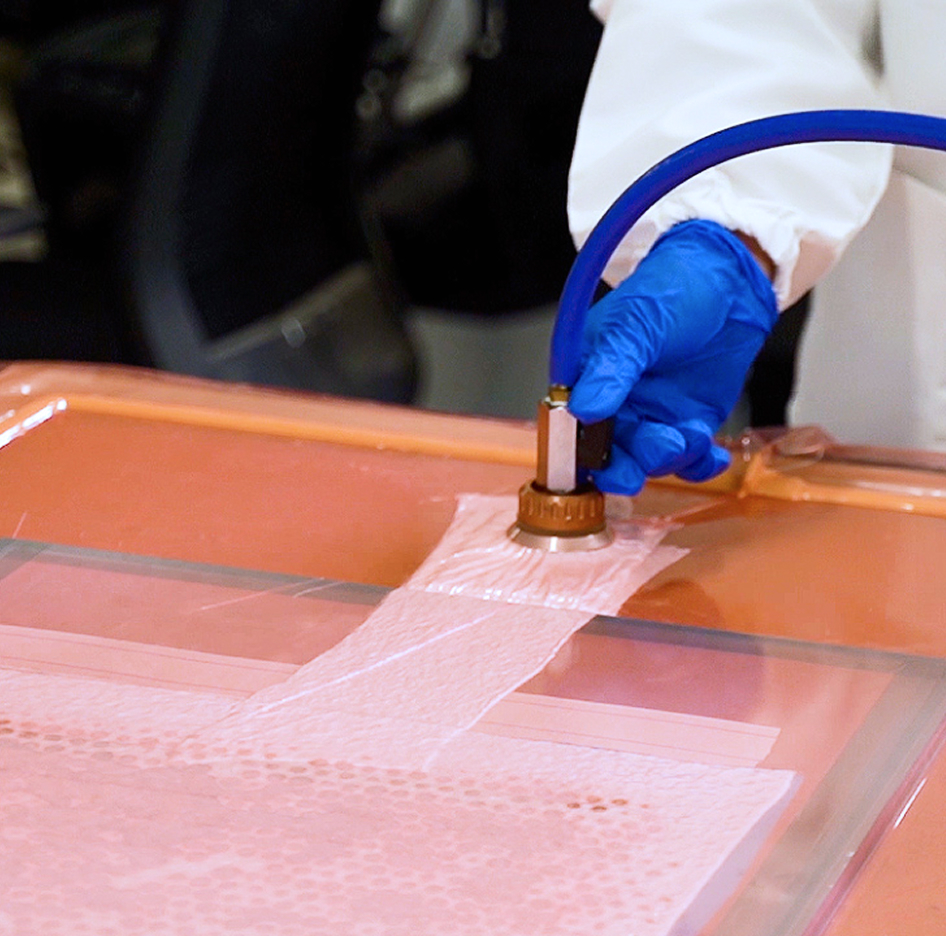
Pollutions from property of chemicals for changing one or more chemicals or chemical compounds, intended to be used in manufacturing or on an industrial scale to change the composition of chemical(s) or material(s). Scrubber’s used to clean air or various products that leak from the process by removing particulates and/or gases from industrial exhaust streams with using liquid to “scrub” unwanted pollutants from a gas stream. ACE’s Scrubber used to clean air or other gases of various pollutants such as HCI, HNO3 or Alkaline solutions.


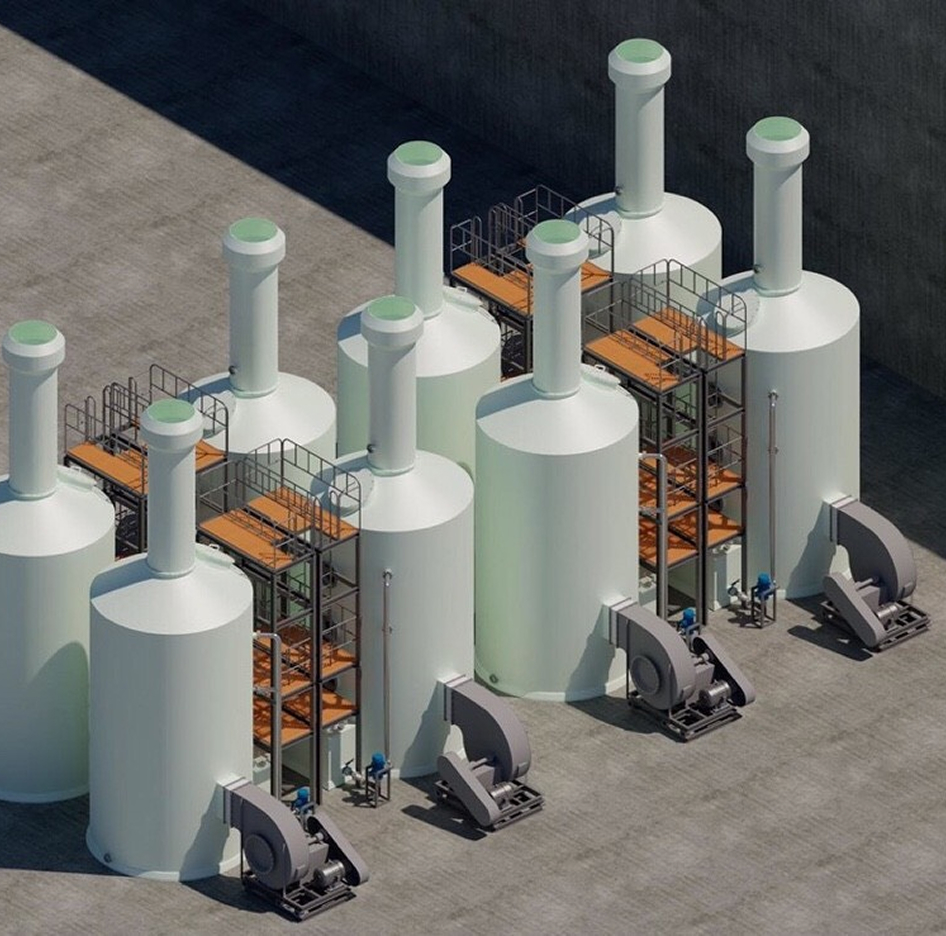
Chemical exhaust gas treatment methods
1
Absorption
Principle: Exhaust gas is passed through an absorption tower, where it comes into direct contact with a liquid solvent (water or absorbing solutions such as alkali, acid, or redox solutions). Pollutant gases are either dissolved or undergo chemical reactions, thereby being removed from the gas stream.
Advantages: High treatment efficiency for gases with high solubility; relatively simple technology, easy to implement in industrial applications.
Disadvantages: Generates secondary wastewater containing pollutants that require further treatment; less effective for gases with low solubility in water.
Example: Absorption of SO₂ in NaOH solution.
2
Adsorption
Principle: Exhaust gas is passed through a solid medium (activated carbon, silica gel, zeolite, etc.), where pollutants adhere to the surface of the adsorbent material.
Advantages: High efficiency in removing volatile organic compounds (VOCs), solvent vapors, odorous gases, heavy metals, and other pollutants.
Disadvantages: Adsorbent materials can become saturated and require periodic regeneration or replacement.
Applications: Treatment of exhaust gases containing VOCs, solvent vapors, and odorous gases such as H₂S and NH₃.
4
Biological Treatment
Principle: Exhaust gas is passed through a packed bed containing microorganisms. These microorganisms use pollutants (VOCs, H₂S, NH₃, etc.) as a nutrient source and degrade them into less harmful substances such as CO₂, H₂O, and inorganic salts.
Advantages:
- Environmentally friendly, does not generate secondary waste.
- High efficiency for odorous gases, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and certain toxic gases.
- Low operating cost, capable of continuous treatment.
Disadvantages:
- Performance depends on the living conditions of microorganisms (temperature, humidity, pH, etc.).
- Suitable only for low to medium pollutant concentrations.
- Requires larger installation area compared to some other technologies.
Applications: Treatment of exhaust gases containing VOCs, solvent vapors, and odorous compounds (H₂S, NH₃, etc.), commonly applied in paint, chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries.
OUTSTANDING ADVANTAGES

Drag the mouse to view the 360° image
thư viện

REGISTER FOR CONSULTATION
Contact ACE Vietnam for consultation and the best solutions!

















